Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 School of Information Engineering, Nanchang University, Nanchang 330031, China
2 Division of Physical Biology, Shanghai Institute of Applied Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Shanghai 201800, China
3 Shanghai Institute of Optics and Fine Mechanics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Shanghai 201800, China
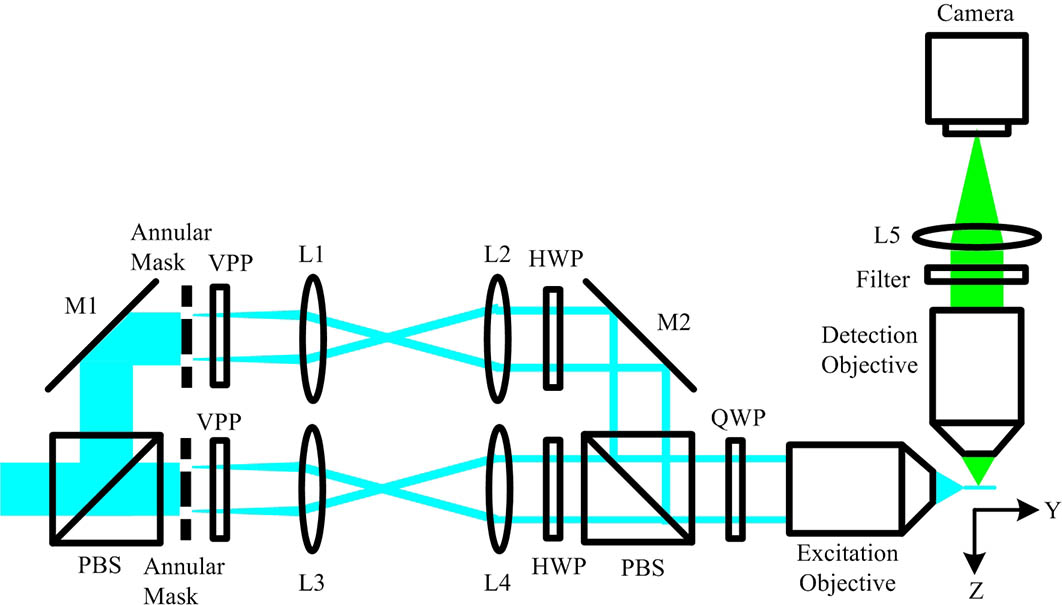
The fluorescence from the out-of-focus region excited by the sidelobes of a Bessel beam is the major concern for light-sheet fluorescence microscopy (LSFM) with Bessel beam plane illumination. Here, we propose a method of applying the subtractive imaging to overcome the limitation of the conventional LSFM with Bessel beam plane illumination. In the proposed method, the sample is imaged twice by line scanning using the extended solid Bessel beam and the ring-like Bessel beam. By subtracting between the two images with similar out-of-focus blur, the improved image quality with the suppression of the Bessel beam sidelobes and enhanced sectioning ability with improved contrast are demonstrated.
180.2520 Fluorescence microscopy 170.6900 Three-dimensional microscopy 100.2980 Image enhancement Chinese Optics Letters
2018, 16(11): 111801
Author Affiliations
Abstract
DNA tetrahedral nanostructures are considered to be new nanocarriers because they can be precisely controlled and hold excellent penetration ability to the cellular membrane. Although the DNA tetrahedral nanostructure is extensively studied in biology and medicine, its behavior in the cells with nanoscale resolution is not understood clearly. In this letter, we demonstrate superresolution fluorescence imaging of the distribution of DNA tetrahedral nanostructures in the cell with a simulated emission depletion (STED) microscope, which is built based on a conventional confocal microscope and can provide a resolution of 70 nm.
110.0180 Microscopy 100.6640 Superresolution 180.2520 Fluorescence microscopy Chinese Optics Letters
2014, 12(4): 041101
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Shanghai Institute of Optics and Fine Mechanics Chinese Academy of Sciences, No. 390, Qinghe Road, Jiading P. O. Box 800-211, Shanghai 201800, P. R. China
2 State Key Laboratory of High Field Laser Physics Shanghai Institute of Optics and Fine Mechanics Chinese Academy of Sciences, No. 390, Qinghe Road, Jiading P. O. Box 800-211, Shanghai 201800, P. R. China
Published 15 August 2012 Recently, we theoretically demonstrate that utilization of silica nanobeads co-doped with Cy3 and Cy5 molecules instead of single dye molecules as fluorescent labels can enable optical resolutions far beyond the diffraction-limit. Here, we show that by combining the 4Pi microscopy and the novel fluorescent label, it is possible to completely suppress the sidelobes in 4Pi focal spot and significantly enhance the optical resolution in the axial direction.
Fluorescent dye 4Pi microscopy far-field imaging super-resolution confocal Journal of Innovative Optical Health Sciences
2012, 5(3): 1250016
1 中国科学院上海光学精密机械研究所强场激光物理国家重点实验室, 上海 201800
2 中国科学院上海光学精密机械研究所, 上海 201800
20世纪末、21世纪初,生命科学发展势头迅猛。三维光学显微成像技术由于能够对活体细胞内的一系列生命活动过程实施三维动态成像而倍受关注。然而,传统的基于线性荧光激发方案的共焦成像技术由于受到光学衍射极限的限制,其横向与纵向分辨率都是在数百纳米左右的量级,仍未能满足生命科学家的普遍需求。利用各种非线性光学荧光激发方案,打破光学衍射极限已经被实现,然而目前这些非线性光学成像方法在光源选择、成像光路等方面均较为复杂与昂贵。通过构筑一种具有奇异非线性光学特性的纳米粒子,在一台普通的光学显微镜上仅仅对荧光分子进行线性光激发即可实现三维远场光学超分辨成像——生命科学家长期来的梦想正有望被实现。
远场光学成像 光学衍射极限 非线性光学





